Search
Presentation Details
| Preoperative frailty screening: De novo process implementation |
| Joan Irizarry-Alvarado Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States |
BACKGROUND: Our outpatient preoperative clinic started in 2007. We see 100% of the surgical population (~18,000/yr) since 2014. In this quality improvement project we identified a gap in quality whereby frailty screening was not being performed. Goal of this project was to implement a frailty screening process in 12 months' time. METHODS: We chose the orthopedic and neurosurgical patients. Inclusion criteria were: 18 y/o and older, total hip/knee arthroplasties and spine procedure (without active septic processes and/or myelopathic pathology). We screened with clinical frailty scale (CFS), Duke Activity Status Index (DASI) and preoperative nutrition score (PONS). There were 2 groups: elderly (>70 y/o) and non elderly (<70 y/o). Frailty was defined as CFS > 3 and/or DASI ≤ 25 and, a positive PONS was considered at risk. Outcome metrics: 30 day mortality, 30 day readmission, non-home discharge (NHD) and length of stay (LOS). Metrics were compared with a non frail control group (i.e. CFS ≤ 3 and/or DASI ≥ 25). A patient brochure education program was started for those at risk to assist in their physical conditioning and nutrition. The physical conditioning brochure has at home full body exercises with resistance bands. The nutrition brochures inform on increasing dietary protein intake and a list of commercially available nutritional supplements. RESULTS: Data collection began on November 1, 2022. A total of 470 patients, of which 184 were elderly and 286 were non elderly. Data shows if CFS ≥ 3 or DASI ≤ 25, the longer the LOS in both groups. Elderly population had a higher incidence of increased NHD. Nutrition screening was initiated clinic wide on July 1, 2023. Preliminary data collection of malnutrition showed that patients with a positive PONS questionnaire had higher LOS and NHD. CONCLUSIONS: Implementation of an inexpensive intervention can be a useful to help those with frailty and malnutrition risk. 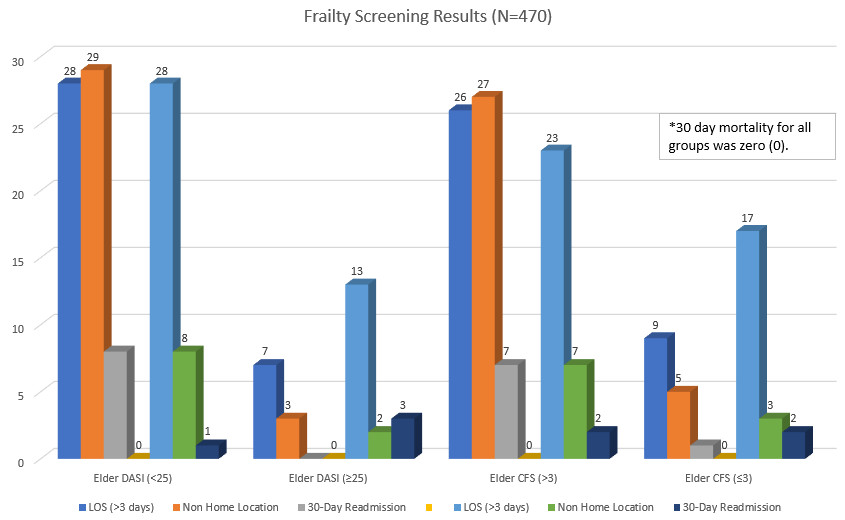 |